Exploring the Dark Side of Crossbreeding Experiments
Written on
Chapter 1: The Ethics of Crossbreeding
Scientific advancements often lead to intriguing innovations, yet they can also delve into ethically questionable territories. One such area is the crossbreeding of different species, where genetic material is combined to produce unique hybrids. This practice can yield both beneficial outcomes, like the beefalo, as well as unsettling ones, such as the human-pig hybrid. These experiments not only create new species that amalgamate traits from both parents but also prompt debates surrounding ethical considerations and animal welfare.
The first video, "Top 10 Crossbreeding Experiments From Hell," dives into the most controversial crossbreeding experiments, showcasing some of the most bizarre outcomes in genetic manipulation.
Section 1.1: Zonkeys and Zedonks
Zonkeys and zedonks have existed for quite some time, originally referenced in Charles Darwin's "Origin of Species" from 1859. The zonkey results from a male zebra mating with a female donkey, while a zedonk is the offspring of a male donkey and a female zebra. These hybrids exhibit traits from both species, including the zebra's striking black-and-white stripes and the donkey's robust physique.
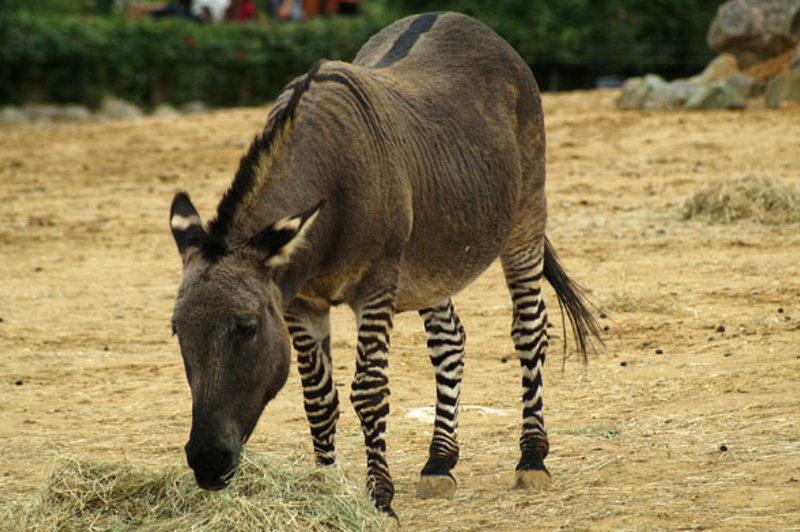

Source: The Atlantic
Despite their intriguing appearance, the behavior of zonkeys and zedonks reflects their wild zebra ancestry, which can manifest as aggression. However, they also possess useful traits, such as the endurance of a donkey coupled with the speed and strength of a zebra, making them potentially valuable as work animals.
Section 1.2: The Geep Phenomenon
A geep, also known as a shoat, is a rare hybrid resulting from the mating of a goat and a sheep. This unusual creature has captivated public attention, particularly due to a famous case involving a goat breeder named Catherine Bell, who inadvertently created a geep named Spring Rose.
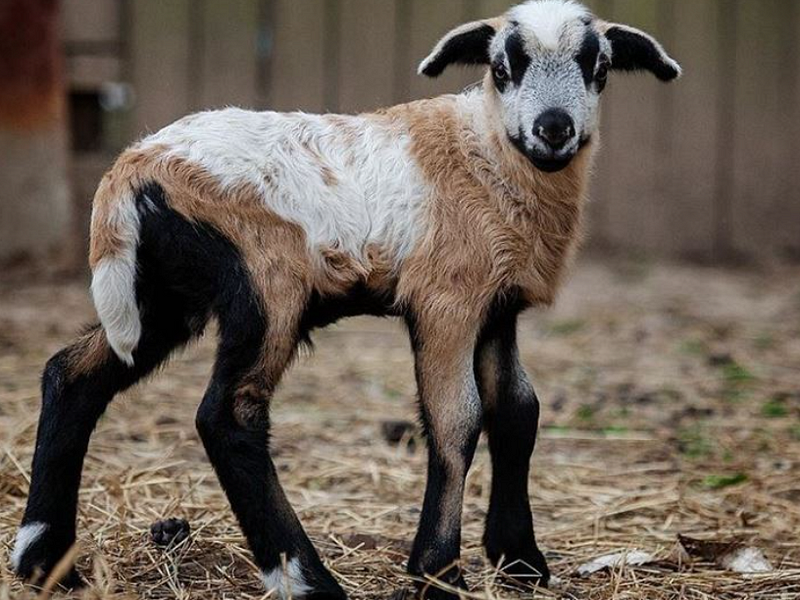

Source: earth.com
Spring Rose showcased a mix of both parent species' physical characteristics, prompting DNA tests that confirmed her hybrid status. Beyond their distinctive appearance, geeps inherit behavioral traits from both goats and sheep, leading to a fascinating blend of social and curious tendencies.
Chapter 2: Controversial Hybrids in Focus
The second video, "Top 20 Crossbreeding Experiments from Hell!" explores even more bizarre hybrids and their implications, providing a deeper look into the world of crossbreeding.
Section 2.1: The Beefalo
Beefalo, a hybrid of domestic cattle and American bison, was developed in the 1970s to combine the best attributes of both animals. Farmers aimed for a breed that possessed the bison's resilience and the meat quality of cattle.
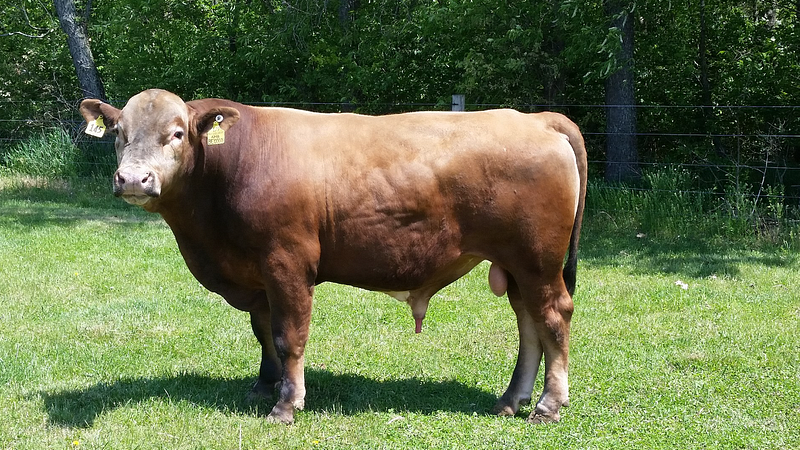

Source: Wikipedia
These hybrids are more adaptable to harsh climates due to their bison lineage, and they are also known for higher fertility and disease resistance. Despite their advantages, ethical concerns arise regarding their breeding practices and the implications for both parent species.
Section 2.2: The Naruga Discovery
In 1984, an intriguing discovery was made in the frigid waters of West Greenland when three unusual whales were found, exhibiting characteristics of both belugas and narwhals. This led to further analysis, revealing that one of the whales was a naruga, a hybrid of a female narwhal and a male beluga.
Source: Vice.com
The unique skull of this creature exhibited features from both species, leading scientists to confirm the existence of this hybrid. This finding highlighted the potential for reproduction between species with differing characteristics.
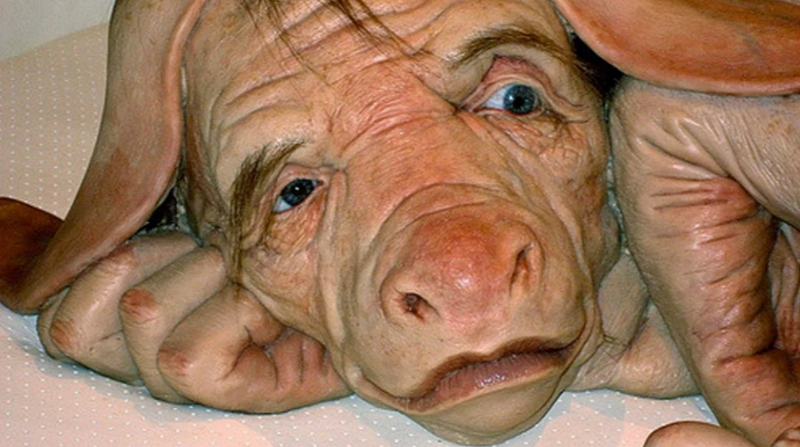
Section 2.3: The Human-Pig Hybrid Experiment
The human-pig hybrid project aimed to cultivate human organs within pigs to address the shortage of transplantable organs. By introducing human stem cells into a pig embryo, researchers sought to create a chimeric embryo capable of developing human-compatible organs.
The ethical implications of this experiment are profound. While it showcased the potential for groundbreaking scientific advancements, it also raised questions about the morality of creating entities that blur the line between species. As such, the experiment was halted before a fully developed brain could form, highlighting the complexities and ethical dilemmas inherent in hybrid research.