Understanding the Expansion of the Universe and Its Effects
Written on
Chapter 1: The Nature of Cosmic Expansion
A subscriber recently posed an intriguing question on my Ukrainian channel: "If the universe is indeed expanding, why do we observe that only the distances between galaxies are increasing, while the distance between closer celestial bodies, like the Earth and the Moon, remains constant?" Additionally, they wondered about the mechanics behind galaxies merging.
In reality, space is expanding in all areas, including between you and the device you are using to read this. However, there are two primary reasons why we don't perceive this expansion in nearby objects. The first reason relates to Hubble's law, which states that the rate at which distances between objects increase depends on their separation.
To illustrate this, consider a balloon on which you've marked four points: two points close to each other and two more that are farther apart.
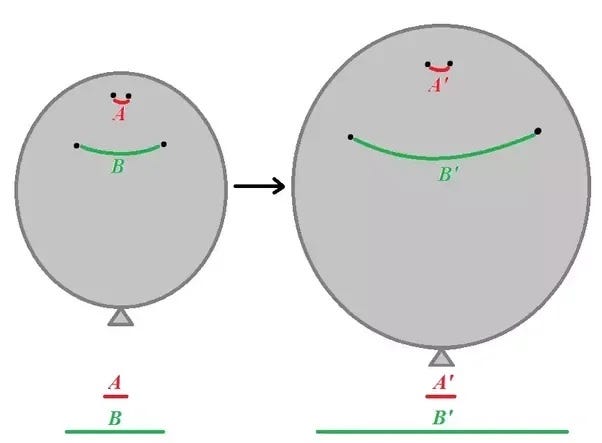
As you inflate the balloon, you'll notice that the distance between the first pair of dots changes only slightly, while the distance between the second pair increases significantly. This phenomenon occurs because space expands uniformly; the greater the distance, the more pronounced the expansion effect. The same principle applies to our universe!
For example, if two points are separated by one parsec (about 3.26 light years), they will drift apart at a rate of merely 7 centimeters per second due to galactic expansion.
Section 1.1: The Earth-Moon Distance Explained
Now, let’s focus on the Earth-Moon distance, which averages around 384,400 kilometers. According to Hubble's law, the Moon is receding from the Earth at an incredibly slow rate of approximately 0.000000009 km/h. This means that it would take around 12,000 years for the distance between the Earth and the Moon to increase by just 1 kilometer.

Source: youtube.com
While 12,000 years might seem insignificant on an astronomical scale, the second factor is crucial: gravity! The Earth, the Moon, and all bodies within our solar system are held together by gravitational forces, which counteract any effects of cosmic expansion. In essence, whenever the Moon drifts away from the Earth or the Earth from the Sun, gravity pulls them back into alignment. At such close ranges, gravitational forces are sufficiently strong to keep everything bound together.
Section 1.2: The Dynamics of Galaxy Collisions
This gravitational interplay is also why galaxy collisions occur. Galaxies can collide when their mutual gravitational attraction overcomes the rate at which space is expanding between them.
Chapter 2: Exploring More Cosmic Phenomena
In this video, "If the Universe is Expanding, Where is the Centre?" we delve deeper into the implications of cosmic expansion and address common misconceptions.
The second video, "If the Universe is Expanding, Then Why Do Galaxies Collide?" explores the fascinating dynamics of galaxies interacting within the ever-expanding universe.
If you enjoy learning about space, feel free to clap for more articles in your feed! Subscribe to our channel and don't hesitate to ask your questions; I will be happy to address them in future posts.